24 Jul The Anatomy of a Coffee Bean: Exploring the Inner Workings of Your Favorite Brew

Coffee is a beloved beverage enjoyed by millions around the world, known for its rich aroma and invigorating flavor. But have you ever wondered about the journey of a coffee bean, from its humble beginnings as a seed to the perfect cup of coffee? In this article, we will delve into the anatomy of a coffee bean, exploring its structure, composition, and the factors that influence its taste. So grab a cup of your preferred brew using your favorite coffee brewing accessories and join us on this fascinating journey!
Coffee Plant and Bean Formation: a. Coffee Plant: The coffee bean comes from the Coffea plant, a tropical evergreen shrub. We’ll briefly explore the different species and their cultivation. b. Bean Formation: Understanding how coffee cherries grow and develop is essential. We’ll explore the flowering, pollination, and fruiting stages that lead to the coffee bean’s formation.
External Structure of a Coffee Bean: a. Seed Coat: Also known as the parchment, this thin layer covers the coffee bean and protects it during growth. b. Silverskin: A delicate layer that clings to the bean, the silverskin is removed during processing. c. Shape and Size: Coffee beans vary in shape and size depending on the species. We’ll discuss the differences between Arabica and Robusta beans.
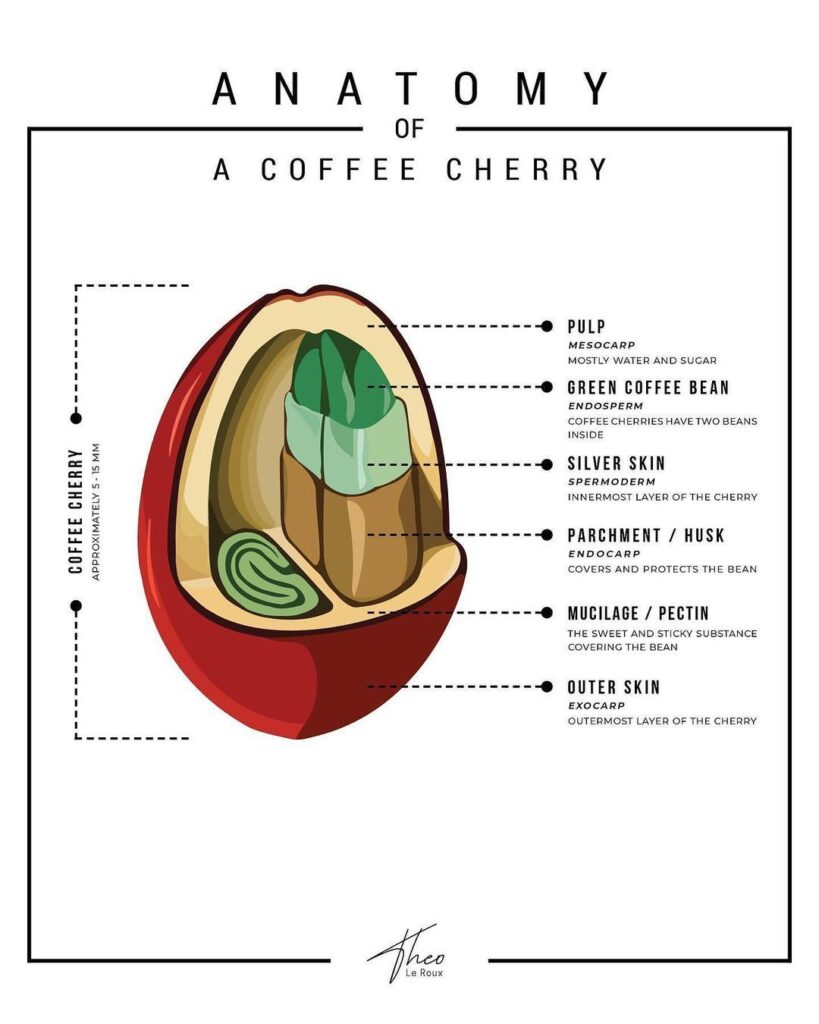
Internal Structure of a Coffee Bean: a. Endosperm: The endosperm forms the bulk of the coffee bean and contains carbohydrates, proteins, and oils. b. Embryo: Also known as the coffee germ, the embryo is the potential coffee plant within the bean. c. Moisture Content: We’ll explore the ideal moisture content of a coffee bean and its impact on flavor and quality.
Chemical Composition of a Coffee Bean: a. Caffeine: Coffee is renowned for its caffeine content. We’ll discuss the role of caffeine in coffee and its effects on the body. b. Acids and Sugars: Coffee beans contain various acids and sugars that contribute to its flavor profile. c. Lipids and Aromatics: The lipids and aromatic compounds in coffee beans are responsible for the delightful aromas and complex flavors.
Roasting and Flavor Development: a. Roasting Process: We’ll briefly touch upon the stages of coffee bean roasting and its impact on flavor. b. Maillard Reaction: The Maillard reaction plays a crucial role in developing the flavors and aromas during the roasting process. c. Flavor Profiles: Different roasting levels result in distinct flavor profiles. We’ll explore the differences between light, medium, and dark roasts.
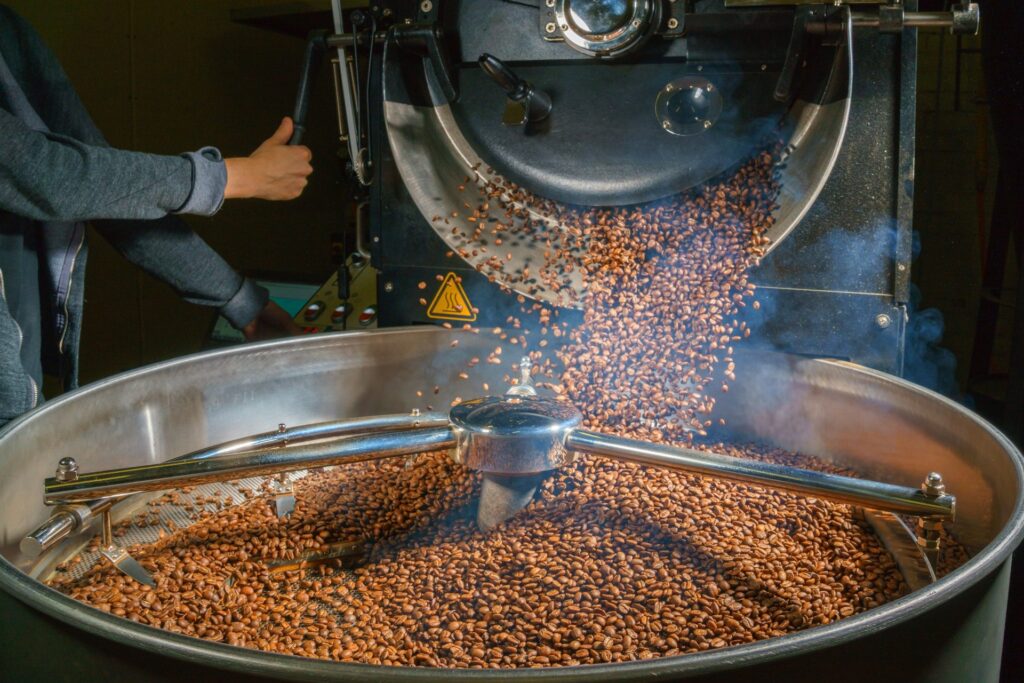

Understanding the anatomy of a coffee bean provides a deeper appreciation for the art and science behind your favorite cup of coffee. From the plant to the roasting process, every step influences the final product’s taste, aroma, and complexity. So the next time you sip your coffee, take a moment to appreciate the intricate journey of those humble beans that bring you so much joy. Please visit café-brew.com for a full range of coffee percolators, pour over coffee makers and permanent coffee filters for all of your coffee brewing needs!





Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.